Understanding Hormonal Birth Control Methods
Learn about hormonal birth control methods including pills, patches, rings, injections, and hormonal IUDs. Discover how they prevent pregnancy and what side effects to expect.
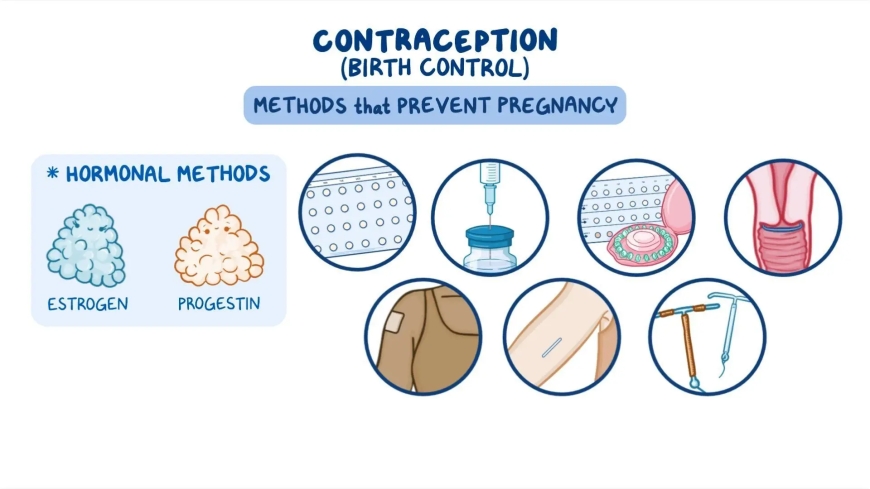
Hormonal birth control methods use synthetic hormones to prevent pregnancy by regulating or stopping ovulation, thickening cervical mucus to block sperm, and thinning the uterine lining to prevent implantation.
These mechanisms work together to create multiple barriers to fertilization and pregnancy, making hormonal contraception highly effective when used consistently and correctly. Common hormonal methods include birth control pills taken daily, skin patches replaced weekly, vaginal rings inserted monthly, injections administered every few months, and hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs) that provide long-term protection.
Beyond preventing pregnancy, many users benefit from more regular menstrual cycles, lighter periods, and reduced menstrual cramps or acne. However, hormonal contraceptives can sometimes cause side effects such as mood swings, weight gain, headaches, or nausea, which vary in intensity from person to person.
Because every individual’s body responds differently to hormones, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to choose the most suitable hormonal birth control method tailored to your medical history, lifestyle, and personal preferences.











